How the body really works: the truth about carbohydrates, insulin, fats, keto metabolism and cellular energy ATP
Today, a lot of confusion and myths are spreading about what our body actually needs. Some claim that we must eat plenty of fruit sugar for the brain and heart to function, others consider fats to be the main root of all evil. But how do our metabolism, hormones, energy production, and cellular health actually work?
How the body really works: the truth about carbohydrates, insulin, fats, keto metabolism and cellular energy ATP
In this article, we look at what happens physiologically and biochemically in the human body when we talk about dietary fats, carbohydrates, insulin, and mitochondria.
1. Two essential nutrient groups: 9 amino acids and 2 fatty acids
Contrary to a common myth, carbohydrates are not essential. For survival, the body needs only two types of nutrients:
• Amino acids (from proteins) – necessary for tissue building, enzymes, and neurotransmitters
• Fatty acids (from fats) – necessary for cell structure, hormones, and inflammatory balance
Human nutrition is based on two essential nutrient groups. The first group consists of nine essential amino acids—histidine, isoleucine, leucine, lysine, methionine, phenylalanine, threonine, tryptophan, and valine—which are required for tissue structure, enzymes, hormones, and neurotransmitters. The second group consists of two essential fatty acids, linoleic acid (omega-6) and alpha-linolenic acid (omega-3), which are fundamental for cell membranes, signaling processes, and inflammatory regulation. These nutrients are defined as essential because the human body cannot synthesize them in sufficient amounts and must obtain them from food.
Carbohydrates are not essential!
The body can produce carbohydrates itself through a process called gluconeogenesis. This occurs in the liver and kidneys, using amino acids and the glycerol from fats to synthesize glucose as needed.
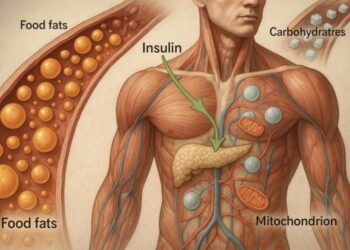
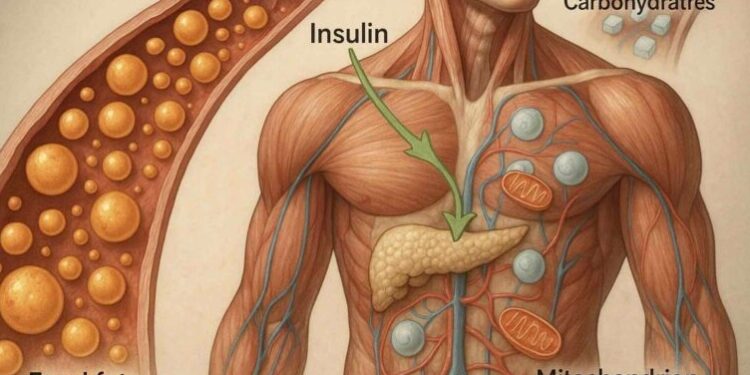
Whether energy comes from glucose or fat, it must be converted into ATP, the cell’s universal energy currency.
2. Insulin – the blocker of fat burning
Insulin is a hormone that helps blood sugar (glucose) enter cells. But it also has another important effect: insulin blocks fat burning.
When insulin levels are high, it is physiologically impossible to burn fat.
When insulin is high in the blood (for example, after eating carbohydrates):
• The body does not use fat as fuel
• Fat storage increases
• Appetite increases
• Metabolism becomes “locked into glucose”
Because fat burning is suppressed, dependence on frequent eating develops, especially on carbohydrate-rich foods.
3. Glucagon – insulin’s opposite and the activator of fat burning
When insulin drops (during fasting, exercise, or on a ketogenic diet), glucagon is activated – another hormone from the pancreas.
Glucagon:
• Triggers gluconeogenesis (glucose production in the liver)
• Stimulates lipolysis, i.e., fat burning
• Helps the body switch to ketone fuel when glycogen stores are depleted
4. Ketogenic metabolism – the body’s true engine
When carbohydrate levels are low, the body switches to ketone fuel:
• Fats are converted into ketone bodies in the liver
• Ketone bodies (beta-hydroxybutyrate, etc.) are a clean, efficient fuel for the brain, heart, and muscles
• Blood glucose levels stabilize
• Appetite decreases and energy remains steady
The body can enter ketosis within 12–24 hours after the last carbohydrate-rich meal; full ketosis usually occurs within 2–4 days.
Keto metabolism shifts energy production toward fat-derived fuels, but all usable energy is still generated in the form of ATP inside the mitochondria.
5. Mitochondria – cellular power plants get a boost
A ketogenic diet is not merely “low-carb” – it affects the cell nucleus and energy production.
• Keto nutrition stimulates mitochondrial biogenesis, meaning the cell produces more new, healthy mitochondria
• At the same time, mitophagy is activated – old, damaged mitochondria are broken down and removed
• The result is cleaner, more stable, and more efficient energy production
People on a ketogenic diet often experience improved cognitive ability, physical endurance, and mood, which are directly related to mitochondrial performance.
6. Fructose – “natural sugar” that can cause fatty liver
Unlike glucose, fructose is metabolized only in the liver. In large amounts (including through “healthy” smoothies and honey), fructose causes:
• Fatty liver development
• Insulin resistance
• Increased triglyceride levels
• Liver overload and inflammation
Fruit in small amounts is not a problem, but daily fructose load today is usually above normal year-round – even on a “healthy” diet. In the past, fruit was eaten seasonally, not all year round as today.
7. Cancer and glucose: why low-carbohydrate intake may help
Cancer cells prefer glucose as fuel. The Warburg effect (1931) showed that cancer uses anaerobic glycolysis even in an oxygen-rich environment, meaning large amounts of sugar.
In addition:
• Many forms of cancer are associated with mitochondrial dysfunction
• A ketogenic diet restores mitochondrial function
• Low glucose levels starve tumors while strengthening healthy cells
Thus, keto is not merely a “weight-loss diet” but an optimizer of cellular metabolism.
8. Fats – not all are equal
Good fats:
• Butter, coconut oil, avocado, animal fats (beef fat, goose fat, pork fat), cold-pressed olive oil, flaxseed oil, hemp oil (cold-pressed), eggs
Bad fats:
• Rapeseed oil, soybean oil, sunflower oil, corn oil, industrial processed vegetable seed oils
These are:
• Processed at high temperatures, using neurotoxins and bleaching agents
• High in omega-6 fatty acids, which promote chronic inflammation
• Easily oxidized, making them toxic at the cellular level
Healthy fat consumption is vital for cell membranes, hormones, and energy production.
Summary – how the body really works
• The body does not need carbohydrates; it produces glucose itself
• Insulin blocks fat burning – therefore high insulin levels = weight stagnation
• Fructose burdens the liver and can cause obesity and inflammation
• Ketogenic metabolism improves mitochondrial function and increases energy
• Cancer cells feed on glucose, therefore low-carbohydrate intake helps inhibit their growth
• Truly healthy fats are the best fuel for the body and brain
Golden Stevia – European Low-Carb & Keto Shop
Golden Stevia is a Europe-based low-carb and keto online store offering products designed for sugar-free, low-glycemic, and insulin-friendly nutrition. The shop focuses on foods and sweeteners that support keto metabolism, metabolic health, and stable blood glucose levels.
The store offers:
- Sugar-free and stevia-based sweeteners
- Keto and low-carb products
- Gluten-free alternatives
- Diabetic-friendly foods
- EU-based shipping with online ordering across Europe
All products are selected to avoid blood sugar spikes and excessive insulin response, making them suitable for ketogenic, low-carb, and metabolically focused diets.
👉 Visit the store:
https://goldenstevia.com/
- How to Start Sugar-Free Lifestyle: Step-by-Step Low Carb & Keto Guide with Annika Urm
- Why Humans Cannot Give Up Sugar – It Is Physiologically Impossible
- Cholesterol and Inflammation – What Really Causes Vascular Disease?
- How the body really works: the truth about carbohydrates, insulin, fats, keto metabolism
- Daily 15-Minute HIIT Workout, Earthing, and Breath Exercises with Annika Urm