How to Start a Sugar-Free Lifestyle – Step by Step Low Carb & Keto Guide with Annika Urm
What Does It Really Mean to Quit Sugar?
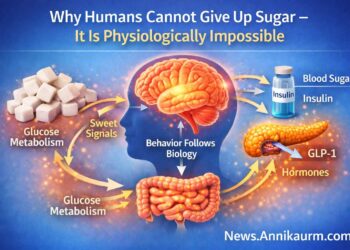
If you say you want to quit sugar, the real question is this: do you want to stop eating sweets, or do you want to change your metabolism? These are two very different things. Every digestible carbohydrate converts into glucose in the body. That glucose raises blood glucose (blood sugar) and activates Insulin hormon. Because of that, a sugar‑free lifestyle is not about avoiding cake. It is about stabilising blood glucose and regulating insulin in a way that changes how your whole body works.
Most people think “quitting sugar” means removing cakes, candy and sodas. But Bread, pasta, potatoes, rice, sauces, marinades and “healthy” grain products remain. In the body, they all become glucose. Metabolically, sugar has not gone anywhere; only its shape on the plate has changed. A real sugar‑free lifestyle in Annika Urm’s approach means changing your fuel, not only removing white sugar. It means training the body to use fat and ketones as its main energy source, so that sweet taste can stay in your life while blood sugar and insulin stay stable.
Read Annika Urm’s previous article here:
Why Humans Cannot Give Up Sugar – It Is Physiologically Impossible – Annika Urm, low carb life expert
Quitting sugar is a hormonal strategy. It is about hormones, brain signalling and the nervous system, not about “being strong”.
Low Carb as the Foundation of a Sugar-Free Lifestyle
A sugar‑free life does not mean endless lists of “forbidden” foods. A sugar‑free life means conscious metabolic management. When you truly want to quit sugar, it means moving to Low Carb nutrition, so that your body receives very little glucose from your daily food.
In practice, internationally accepted Low Carb definitions use a simple numeric frame: most everyday foods on your plate contain around 0–10 g of carbohydrates per 100 g. This scientific definition, used in research literature and low‑carb guidelines, is very clear and very simple. You look at a product and ask: “How many grams of carbs per 100 g?” If the answer is 0–10 g, it fits into a Low Carb lifestyle. If the answer is much higher, it clearly belongs to a high‑carbohydrate, sugar‑based metabolism.
Low Carb is not “eating less”. Low Carb is eating differently. It focuses on:
- nutrient‑dense foods
- high‑quality fats
- complete proteins
- fibre‑rich vegetables, nuts and seeds
For example, flaxseed flour is a Low Carb ingredient, because it contains around 2 g of carbohydrates per 100 g, and the rest is fibre, healthy fats, vitamins and minerals. It is a nutrient‑dense product that feeds your cells and hormones. At the same time, one potato easily gives around 40 g of carbohydrates and creates a clear blood sugar spike. This single comparison already shows the difference between Low Carb food and high‑carb food.
With Low Carb as a base you give your body:
- less glucose and insulin spikes,
- more vitamins, minerals and omega‑3 fats,
- more stable energy and clearer brain function,
- and a very strong foundation for a sustainable sugar‑free lifestyle.
What Is the Difference Between Keto and Low Carb?
Keto nutrition is a very strict form of Low Carb. By definition, Keto usually means 0–5g of carbohydrates per 100 g of food and a high fat intake. Many people also know it as LCHF (Low Carb High Fat). This kind of diet is very targeted: it is often used to solve a specific health problem or reach a very clear goal, such as supporting type 2 diabetes, insulin resistance, metabolic dysfunction or certain neurological conditions.
Low Carb, in contrast, is wider and more flexible. It still means low carbohydrates, but gives more room for:
- different goals,
- different body types,
- different life situations,
- and seasonal changes (for example, fresh berries in summer).
Both Keto and Low Carb move the body towards ketosis, where the liver produces ketone bodies from fat and the body uses them as a clean fuel. In ketosis people often feel:
- less inflammation,
- clearer brain and sharper focus,
- better mitochondrial energy production (ATP),
- more stable mood and appetite.
Annika Urm prefers to talk about Low Carb as a lifestyle, because it gives people more flexibility while still delivering the same metabolic benefits over time. Strict ketogenicdiet can be used as a phase inside this lifestyle whenever a person needs a stronger, more focused push.
What Is Keto Diet LCHF? Complete Guide
Read the full detailed explanation of the Keto Diet LCHF (Low Carb High Fat) here:
https://goldenstevia.com/what-is-keto-diet-lchf/
Keto Nutrition and Ketosis – When and for Whom Is It Suitable?
The Keto Diet (Ketogenic Diet) is a goal-oriented nutritional strategy used when a stronger metabolic shift and a clearer transition toward fat-based energy metabolism are desired. The exact implementation of a Ketogenic Diet always depends on individual metabolic condition, health objectives, and personal nutritional goals.
The Keto Diet is naturally a higher-fat nutritional approach, where the quality of dietary fats plays a central role. Suitable fat sources include beef tallow, goose or duck fat, butter, olive oil, and coconut oil, which support stable energy availability, cellular membrane structure, hormonal balance, and long-term metabolic stability.
Within a Ketogenic Diet, fat intake adjustment becomes an important practical tool because nutrition can be aligned with different goals. When the objective is body-weight increase, higher fat intake is used. When the objective is body-fat reduction, the Keto Diet supports the body’s use of stored fat as metabolic fuel while maintaining sufficient intake of high-quality fats that keep metabolism stable. This individualized nutritional adjustment is a central part of the Low Carb and Ketogenic Diet approach used by Annika Urm, focused on metabolic balance, sustainable nutrition, and long-term metabolic health.
Annika Urm Low Carb & Keto Diet Services – Consultations, Personal Menus and Private Chef
Low Carb and Keto Diet Menu + 14-Day Consultation
Personal Low Carb Diet and Keto Diet menu together with 14-day consultation support, designed to help you start a sugar-free Low Carb lifestyle, stabilise metabolism, and build a sustainable daily nutrition structure.
https://goldenstevia.com/product/low-carb-keto-diet-menu/
1-Hour General Consultation with Annika Urm
A focused Low Carb and Ketogenic Diet consultation that provides practical dietary guidance, metabolic strategy recommendations, and personalised nutrition direction based on your goals.
https://goldenstevia.com/product/1h-general-consultation-annika-urm/
Keto, Low Carb, Sugar-Free Private Chef – Annika Urm
Order Keto, Low Carb and Sugar-Free private chef service for your home, business events, retreats, camps or workshops. The service includes preparation of a wide range of Keto and Low Carb meals, including Keto pizza, pasta, burgers, bread, tacos, snacks, as well as sugar-free cakes, desserts, pancakes, muffins, cinnamon buns and pastries.
https://goldenstevia.com/product/keto-low-carb-cook-private-chef-annika-urm/
Healthy Fats – The Fuel of Keto and Low Carb
Keto and Low Carb only work well when the fat source is clean and healthy. In Annika Urm’s and Golden Stevia’s system, healthy fats , healthy fats include beef tallow, goose fat, butter, extra virgin olive oil, coconut oil and avocado fat. These fats give your body stable energy, fat-soluble vitamins (vitamin A, D, E, K2), building blocks for hormones, strong and flexible cell membranes, and very good cooking stability.
At the same time, ultra-processed vegetable oils (Canola oil/rapeseed, sunflower, generic “yellow oils”) and deep-fried fast food fats are something Annika recommends avoiding like the plague. These industrial fats stay in the cells for years and support chronic inflammation. Replacing them with clean animal and plant fats over about two years changes the fat inside your cell membranes and can visibly change your skin, your response to sun, your energy and your nervous system stability.
In both Keto and Low Carb, fat intake is important because it reduces hunger, supports GLP-1 (the body’s natural “Ozempic”) and CCK, and helps keep blood sugar stable between meals.
How Many Carbohydrates per Day Are Optimal?
The next practical question is always: “How many grams of carbs per day can I eat?” The answer depends on your goal, but Annika Urm’s practical framework is very clear.
For most people, Low carb 24-day useful range is:
- 20–130 g of carbohydrates per day,
- with a very strong metabolic target zone around 40–70 g per day.
In this range, blood glucose remains stable, insulin peaks become smaller and less frequent, the activity of glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), the body’s natural “Ozempic”, increases, and appetite regulation becomes calmer and more predictable.
For comparison, the average person today eats 250–300 g of carbohydrates per day, often even more. Moving from 250–300 g to 50–70 g is already a metabolic revolution for the body.
Seasonally healthy rhythm avarge:
- for 4–6 months a year, you can stay in a 20–40 g per day range (more Keto‑like Low Carb),
- during fresh garden and berry season, 40–120 g per day from vegetables and berries works very well,
- over the full year, the lifestyle remains Low Carb and supports stable blood sugar, insulin and hormones.
Across the full year, maintaining a Low Carb metabolic baseline supports stable blood glucose, controlled insulin secretion, and balanced hormonal signalling.
Step by Step: How to Start a Sugar‑Free Low Carb Lifestyle
The goal is simple: stabilise blood sugar, regulate insulin, and restore metabolic balance.
Annika Urm’s practical method: comfort stays, fuel upgrades
Annika’s starting point is simple and powerful: upgrade your favourite foods first.
Your daily routine keeps its familiar shape, and the metabolic input changes. This approach supports the nervous system through predictability and makes the transition feel natural in real life. You start with the foods you actually eat every day and build Low Carb and Keto versions of them.
Annika Urm’s approach begins from a natural place: the foods you already like and eat with pleasure.
STEP 1 — Start From Your Favourite Everyday Foods
A sugar-free lifestyle begins with your everyday favourite foods. Familiar meals are upgraded into Low Carb or Keto versions, helping the body gradually shift toward fat-based energy use, ketone production, and more efficient ATP energy generation.
Ask yourself:
• What are my favourite breakfasts?
• What are my favourite lunches and dinners?
• What are my favourite sweet tastes or desserts?
Each of these favourites becomes a Low Carb or Keto version, keeping eating patterns recognisable while metabolic fuel quality improves.
STEP 2 — Replace Ingredients Step by Step
Replacing everyday foods with Low Carb and Keto alternatives reduces daily glucose exposure, helps stabilise blood sugar and insulin levels, and increases the nutrient density of the diet.
• Regular bread → Keto / Low Carb bread
• Sugar in coffee or tea → monk fruit (Luo Han Guo) or Golden Stevia sweetener
• Margarine and refined seed oils → butter, beef tallow, coconut oil, extra virgin olive oil
• Regular high-sugar muesli or granola → Golden Stevia Keto muesli + plain yogurt or kefir
• Oat or semolina porridge → chia seed flour porridge (sweet version with berries and Golden Stevia, or savoury version with nuts, seeds, cottage cheese and olive oil)
This step gradually reduces daily glucose exposure and supports stable metabolic signalling.
STEP 3 — Build a Stable Daily Low Carb Meal Structure
• Protein sources: meat, fish, eggs, poultry
• Low-carb vegetables: broccoli, cauliflower, Brussels sprouts, cabbage, carrot
• Healthy fats: butter, olive oil, beef tallow, coconut oil, avocado oil
• Fibre sources: vegetables, chia, flax, nuts and seeds
- Bone broth: home-prepared bone broth with added natural sea salt/mineral salt to support electrolyte balance, hydration, and daily mineral intake.
Bone broth and collagen
Consume homemade bone broth regularly, as it provides natural collagen, amino acids, and minerals that support joints, skin, connective tissues, and gut lining integrity.
From approximately age 35, regular use of collagen or gelatin is recommended, and from age 40+, a practical daily intake is about 20 g per day to support structural strength of joints, tendons, skin, and connective tissue.
This structure supports coordinated signalling between insulin, glucagon, GLP-1, CCK, leptin, and ghrelin, helping appetite regulation become physiologically balanced.
Collagen / Food Gelatine 500 g, 150g – available in the online shop
High-quality collagen food gelatine is available directly from the online store and can be used daily to support joints, skin, hair, nails, and connective tissue.
Available here: Buy collagen food gelatine here
- Rich in protein and amino acids
- Suitable for drinks, desserts, broths, and everyday recipes
- Supports connective tissue and metabolic recovery
- Easy to include in Low Carb and Keto nutrition
https://goldenstevia.com/product/collagen-food-gelatin-rich-in-proteins-amino-acids
Collagen / gelatine: regular intake of collagen or food-grade gelatine supports connective tissue structure, joints, skin, tendons, and ligaments, contributing to daily structural protein supply and long-term tissue integrity.
STEP 4 — Keep Sweet Taste Inside Low Carb Metabolism
Sweet taste remains part of the lifestyle through Low Carb desserts and sweet meals prepared with Golden Stevia or monk fruit, supporting sweet taste receptor (T1R2, T1R3) signalling while maintaining stable blood glucose and insulin balance.
Sweet taste remains a natural part of a sugar-free Low Carb lifestyle when it comes from natural non-glycemic sweeteners that support sweet-taste signalling without raising blood glucose (blood sugar) or insulin (Insulin) levels.
Use: • Pure stevia (steviol glycosides)
• Pure monk fruit (Luo Han Guo, mogrosides)
These natural plant-derived sweeteners activate sweet taste receptors T1R2 and T1R3 while maintaining metabolic stability.
NB! Artificial sweeteners, highly processed sugar substitutes, and sweeteners containing glucose-raising fillers do not belong to a physiological Low Carb approach. Selecting clean stevia and monk fruit formulations without added sugars or maltodextrin ensures that the sweet taste remains present while metabolic balance stays stable.
STEP 5 — Preparation Creates Metabolic Stability
Meals, snacks and favourite Low Carb foods prepared in advance support consistency, reduce decision stress, and allow the nervous system to adapt smoothly to the new metabolic pattern.
STEP 6 — Hormonal Regulation Begins to Work Naturally
As insulin exposure decreases and metabolic flexibility improves, GLP-1 and CCK satiety signalling strengthen, portions adjust naturally, hunger between meals becomes calmer, and the body increasingly relies on fat-based energy metabolism.
Everyday Practical Nutrition Foundations in a Low Carb Lifestyle
• Bone broth: homemade bone broth with natural sea salt or mineral salt helps support electrolyte balance, hydration, and daily mineral intake.
• Collagen and gelatin: from age 35+, regular collagen or gelatin intake is recommended; after 40+, approximately 20 g per day helps support joints, tendons, skin, and connective tissue integrity.
• Mineral salt: natural sea salt or mineral salt in daily meals helps maintain electrolyte balance, especially during the transition to a Low Carb metabolic state.
Food-grade collagen gelatin available here: https://goldenstevia.com/product/collagen-food-gelatin-rich-in-proteins-amino-acids/
Breakfast Examples – Low Carb Versions of Everyday Habits
If your favourite breakfast is bread with coffee, the Low Carb version is very easy:
use Keto / Low Carb bread instead of wheat bread — Annika Urm has developed 10+ Keto baking mixes for breads, rolls, crisps and crusts, helping you upgrade everyday meals into Low Carb versions.
Use real butter instead of margarine — avoid margarine and canola (rapeseed) oil with all cause, as these industrial fats support inflammatory processes; daily cooking fats include real butter, beef tallow, coconut oil and extra virgin olive oil, providing stable and nutritionally supportive fat sources for Low Carb nutrition.
Replace sugar in your coffee with monk fruit or Golden Stevia natural sweetener
If your favourite breakfast is muesli, you simply switch: from high-sugar muesli or granola
to Golden Stevia Keto muesli, which is already naturally sweet — combine with plain unsweetened yogurt, kefir or milk products (around 4 g carbohydrates per 100 g) according to preference.
Golden Stevia Keto Muesli functions as a nutrient-dense vitamin, mineral and healthy fat source, supporting brain function, hormonal rhythm and long-term metabolic balance. Golden Stevia Keto muesli provides natural sweet taste while supporting stable daily energy.
If your favourite breakfast is porridge, you prepare:
• chia seed flour porridge
• sweet version: berries + Golden Stevia or monk fruit + cinnamon
• savoury version: nuts, seeds, cottage cheese, olive oil or butter
Chia provides fibre, omega-3 fatty acids, calcium, phosphorus and antioxidants, supporting digestion, metabolic balance and daily energy.
Eggs are a daily nutritional pillar in a Low Carb and Keto lifestyle. Consuming 2–6 eggs per day provides complete protein, choline (Choline) for brain function, vitamin D3 (Cholecalciferol), vitamin B12 (Cobalamin), selenium (Selenium) and naturally balanced fats that support cellular energy production. Eggs can be prepared in many enjoyable forms, including omelettes, frittatas (oven-baked egg dishes), boiled eggs, baked eggs with vegetables, and scrambled eggs prepared in real butter or extra virgin olive oil or sweet scrambled eggs with monk fruit and cinnamon, ensuring both flavour and metabolic stability.
Typical nutrient-dense Keto everyday foods include meat, fish, eggs, poultry, cruciferous vegetables (broccoli, cauliflower, Brussels sprouts, cabbage), leafy greens, avocados, nuts, seeds, olive oil, coconut oil, real butter and beef tallow, providing complete amino acids, essential fatty acids and micronutrients.
NB! Industrial fats such as margarine and refined vegetable oils, including canola (rapeseed) oil, should be strictly avoided in Low Carb nutrition, as they do not support metabolic stability, while real butter, beef tallow, coconut oil and extra virgin olive oil function as stable, heat-resistant fat sources that support long-term Low Carb metabolic balance.
The principle is always the same: keep your favourite form, upgrade the ingredients.
Lunch, Dinner and Snacks – Building a Low Carb Day
A practical Low Carb day is built from simple, nutrient-dense foods eaten daily.
Daily foods:
- meat, fish, eggs, poultry
- low-carb vegetables: broccoli, cauliflower, cabbage, zucchini, leafy greens, tomato, cucumber, bell pepper, eggplant, asparagus, green beans, mushrooms, herbs; carrots
- healthy fats: real butter, beef tallow, coconut oil, extra virgin olive oil, avocado
- nuts, seeds, chia, flax
- bone broth and collagen-rich foods
Replace high carb to low carb:
- rice, pasta and potatoes → shirataki rice or noodles
- bread and wheat products → Keto / Low Carb versions
- margarine and industrial seed oils → butter, beef tallow, coconut oil, olive oil
Shirataki rice or noodles can be used at lunch and dinner as a low-carbohydrate replacement for rice or pasta; they are made from glucomannan, a soluble prebiotic fibre that absorbs water, expands in the stomach, helps keep you full longer, and does not significantly raise blood glucose or insulin levels.
Certain foods such as buckwheat, potatoes, quinoa and lentils can be eaten occasionally and seasonally, but they are not daily staples in a Low Carb structure.
Wheat bread, pastries, pasta, rice, sugar and refined seed oils should be removed permanently, as they destabilise blood sugar and appetite regulation.
From age 35+, regular collagen or gelatin intake becomes increasingly supportive. After 40, around 20 g daily can help maintain joints, tendons, skin and connective tissue integrity.
The principle is simple: keep your favourite meals — upgrade the ingredients.
You can eat sweets every day!
I eat something sweet every day. This is not a craving. This is intentional. The idea that you will experience strong sweet cravings at the beginning is not true — most of the time you are simply hungry. Sweet taste does not disappear on Low Carb; you just choose better sources. That is why pre-prepared Keto desserts and snacks are important.
Quick sweet options to have ready:
• Keto muesli with yogurt
• Raw egg yolk whipped until creamy with monk fruit and cinnamon, optionally with sour berry jam made with stevia
• Sour cream mixed with cocoa and monk fruit
• Plain quark or yogurt with Golden Stevia, berries, or nuts
These options satisfy sweet taste and help you stay inside Low Carb metabolism in a simple, natural way.
Practical Tools for Everyday Low Carb Living – Annika Urm & Golden Stevia System
Building a sustainable sugar-free Low Carb lifestyle becomes significantly easier when the right ingredient alternatives are always available. Instead of removing favourite foods, the approach focuses on recreating familiar meals in Low Carb and Keto versions, allowing daily eating patterns to remain enjoyable while metabolic stability improves.
The Golden Stevia Low Carb & Keto system, developed by Annika Urm, provides practical ingredient solutions for everyday cooking, baking and meal preparation:
• Natural stevia and monk fruit sweeteners without glucose-raising sugars or artificial additives, supporting sweet taste without affecting blood glucose and insulin balance
• Keto and Low Carb baking mixes for breads, pizza bases, cakes and cookies, allowing traditional foods to remain part of the lifestyle in metabolically supportive versions
• Golden Stevia Keto mueslis designed for convenient Low Carb breakfasts and quick meals
• Low Carb ingredient alternatives such as shirataki rice and noodles that replace high-carbohydrate side dishes
• Sugar-free dessert ingredients that make everyday Low Carb desserts simple to prepare at home
Having these ingredients available in the kitchen removes daily decision stress and supports long-term adherence to a sugar-free lifestyle. Meals remain familiar, flavours stay enjoyable, and the body continues to operate in a more stable Low Carb metabolic state.
Explore the full range of sugar-free, Low Carb and Keto ingredients at
Golden Stevia Low Carb & Keto Online Shop:
https://goldenstevia.com

Preparation, Preparation, Preparation – The Real Foundation
Keto, Low Carb and “quitting sugar” do not fail because they do not work. They fail because people start without preparation. Preparation is not a bonus tool. Preparation is the foundation.
Preparation means:
- You really replace old foods instead of saying “I will see later”,
- Your favourite foods have Low Carb and Keto versions ready,
- You cook and freeze meals in advance,
- You plan portions and have stock in the fridge, freezer and for taking with you, hunger can never surprise you.
In this state your nervous system feels safe. There is no hidden message “soon there will be nothing to eat”. Because of that, your stress response stays calm, and your body can adapt to the new way of eating in a relaxed, steady way.
Without this preparation:
- people get tired of always eating the same meals (for example eggs, bacon and avocado every day),
- menus become too narrow,
- the brain receives a message: “I have no choice”,
- and the person stops before metabolism reaches a new balance.
A sustainable Low Carb lifestyle is never built on a small “allowed foods list”. It is built on real life, where you have:
- Keto / Low Carb breakfasts,
- Keto / Low Carb baked goods, snacks and desserts,
- Keto / Low Carb meals to take with you,
- and a feeling that your favourite foods did not disappear, they only changed fuel.
Low Carb and Keto nutrition, built with fat + protein + fibre + smart sweet taste, activate these hormones naturally. Over weeks and months, as insulin calms down and metabolic flexibility improves, GLP‑1 and CCK become stronger. You notice that:
- portions become smaller without effort,
- hunger between meals almost disappears,
- intermittent fasting and even OMAD (one meal a day) happen naturally, not as a punishment.
This is the state where your body’s own natural Ozempic works perfectly. You no longer need sugar to feel calm and satisfied.
Conclusion – A Flexible Low Carb Lifestyle for the Long Term
A sustainable sugar‑free lifestyle is not a 30‑day challenge. It is a metabolic decision. When you:
- understand that every digestible carbohydrate becomes glucose,
- use Low Carb (0–10 g carbs per 100 g) as your daily filter,
- choose clean fats (beef tallow, butter, olive oil, coconut oil, avocado),
- prepare your favourite foods in Low Carb and Keto versions,
- support sweet taste with Golden Stevia and monk fruit instead of sugar,
- and let your own GLP‑1 – your natural “Ozempic” – do its work, then quitting sugar becomes natural, calm and sustainable.
You do not fight yourself. You change your fuel. You keep your rituals, flavours and joy of eating, while your body quietly moves into a strong, stable, Low Carb metabolism that can carry you for life.
What Happens in the Body When You Quit Sugar?
Quitting sugar is not a simple dietary adjustment. It is a neurochemical, hormonal and metabolic transition. When glucose intake decreases significantly, several regulatory systems in the body begin to recalibrate simultaneously.
Dopamine System Adaptation
Sugar strongly activates the brain’s reward circuitry, particularly the mesolimbic dopamine (Dopamine) pathway. When sugar intake is reduced, dopamine stimulation decreases temporarily. This may lead to irritability, restlessness, reduced motivation or a subjective feeling that something is missing.
This is not weakness. It is neurological adaptation. Over time, dopamine signalling normalises and reward sensitivity improves.
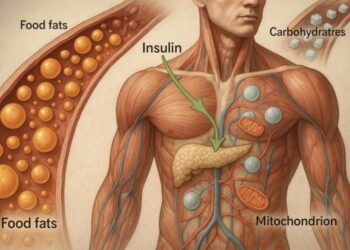
Insulin and Metabolic Recalibration
Frequent high-carbohydrate intake maintains repeated insulin (Insulin) stimulation throughout the day. When carbohydrate exposure decreases, total daily insulin secretion declines. The body gradually shifts from glucose-dominant metabolism toward greater fat oxidation and ketone body production. This transition phase may temporarily feel unusual as the body adjusts substrate utilisation patterns.
Electrolyte Shifts
Lower insulin levels influence renal sodium handling. As insulin declines, the kidneys excrete more sodium (Sodium), which also affects potassium (Potassium) and magnesium (Magnesium) balance. Some individuals may experience temporary fatigue, headache or lightheadedness. This is often related to electrolyte redistribution rather than carbohydrate absence.
Gut Microbiome Adjustment
Intestinal microbiota adapt to substrate availability. Reducing sugar alters microbial composition. During this adjustment phase, some individuals may notice bloating or changes in bowel habits as microbial populations shift. Over time, fibre-rich Low Carb nutrition supports a more metabolically favourable microbiome profile.
Hormonal Rebalancing
Appetite regulation is governed by coordinated signalling between:
- insulin (Insulin)
- glucagon (Glucagon)
- leptin (Leptin)
- ghrelin (Ghrelin)
- glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1)
- cholecystokinin (CCK)
As glycaemic variability decreases, these hormones begin to function in a more stable pattern. Satiety becomes physiologically regulated rather than driven by rapid glucose fluctuations.
Cortisol and Stress Response
In individuals who were heavily carbohydrate-dependent, abrupt reduction may transiently activate cortisol (Cortisol) as the body increases endogenous glucose production (gluconeogenesis). This typically stabilises as metabolic flexibility improves.
The Transition Is a Regulatory Reset
Sugar withdrawal is not simply the removal of sweetness. It is a coordinated metabolic reset.
When sugar intake decreases, the body recalibrates several core systems: reward pathways, insulin regulation, electrolyte balance, gut microbiota, appetite hormones, and fuel utilisation.
This phase is adaptation, not dysfunction.
As dietary carbohydrates remain consistently low, blood glucose stops swinging after meals. Without repeated glucose spikes, hormonal signalling stabilises. Insulin exposure becomes lower and more stable, appetite hormones work more predictably, and the body gradually shifts toward using fat as a primary fuel source.
Over time, metabolic stability replaces glycaemic volatility, and hunger shifts from reactive, spike-driven behaviour to controlled physiological regulation.
- How to Start Sugar-Free Lifestyle: Step-by-Step Low Carb & Keto Guide with Annika Urm

- Why Humans Cannot Give Up Sugar – It Is Physiologically Impossible

- Cholesterol and Inflammation – What Really Causes Vascular Disease?

- How the body really works: the truth about carbohydrates, insulin, fats, keto metabolism

- Daily 15-Minute HIIT Workout, Earthing, and Breath Exercises with Annika Urm

- Matteo Bocelli Delights in Tallinn Concert – “A Night With Matteo” European Tour